In 2012, after moving to the Bay Area, Ashton Braun set out to build a platform that could solve some of the inefficiencies in food and agricultural supply chains. He experienced these inefficiencies firsthand while working as a commodities trader in Singapore, where he saw businesses struggle to overcome the asymmetry of the supply- and demand-side communications.
“The communication challenges were a result of the self-sensitivity of perishable inventories,” Braun told TechCrunch in an email interview. “Removing friction and risk between two businesses transacting in the supply chain was a major problem, and was a primary barrier for a business’s growth. Payment risk and access to working capital was a driving factor behind a business’s ability to build strong relationships or new relationships within the supply chain.”
Braun put his idea on hold for a few years to help a friend, Adam Smith, build the generative coding startup Kite. But in 2018, Braun assembled a team to found the supply chain startup Silo, whose platform structures communications data from food and agricultural businesses and then uses the data to automate those businesses’ workflows.
In subsequent years, Silo expanded into payments products for accounts payable and accounts receivable automation. Now the company offers services to food supply chain businesses for inventory management, ledger accounting and financing.
“Once Silo was in the payment flow, we could pair the data collected from our software with payments products to both underwrite and collect better than any bank,” Braun said. “This is the basis for a number of new services Silo is working on within supply chain finance, logistics coordination and internal workflow automation.”
Braun acknowledges that Silo has competition in the over-$27.2-billion supply chain tech space (see: Pando, Prewave, etc.), but he sees the company primarily competing with legacy, on-premises software and spreadsheets. Supply chain companies are reluctant to change their processes, he tells me — and he’s not the first person to make that observation.
A 2023 survey from PwC found that few companies are using or planning to use technologies to automate and enhance different areas of their supply chain over the next 24 months. At the same time, 86% of respondents said that their organizations should invest more in tech to identify, track and measure supply chain risk.
“Many of the systems and solutions in this industry have been around for over 20 years,” Braun said. “We’re building intuitive solutions on the foundation of modern technology.”
How “modern,” exactly? Well, Silo applies AI to various components of the perishable supply chain, including underwriting, product taxonomy, document extraction and fraud detection. For example, Silo says it uses language models to help customers import unstructured, natural language descriptions of their inventory (e.g., “organic fuji apple, 15 lb”) into a unified, normalized catalog. On the underwriting side, Silo employs several AI models to assess a businesses’ risk and detect anomalies during the funding process.
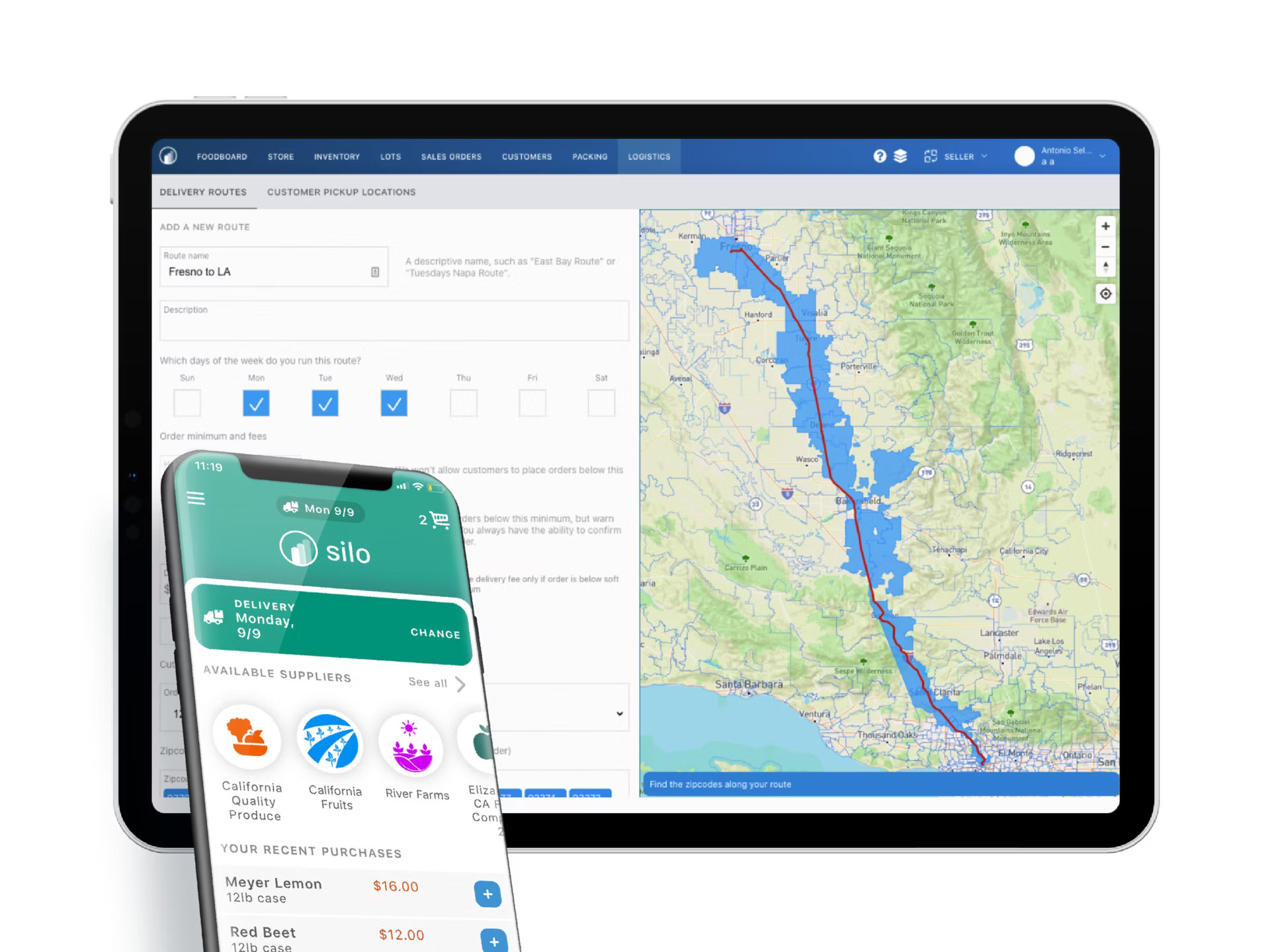
Image Credits: Silo
“In perishables, cash is king and access to working capital to fund inventory supply and operational investments in infrastructure is a constant challenge,” Braun said. “Weather, border controls, freight logistics add an additional layer of complexity that is mostly out of companies’ control, while the high volume of financial transactions that are tracked across paper and disconnected systems make it difficult to track and discern the financial health of a business.”
This AI-forward approach seems to be working for Silo, which has hundreds of customers and revenue that’s grown by more than 100% since December 2022 to “tens of millions” of dollars. Investors seem to be pleased with the strategy as well. Silo, to wit, this week closed a $32 million Series C round led by Koch Disruptive Technologies with participation from Andreessen Horowitz, Haystack Capital, Tribe Capital, Collate Capital and Moore Capital.
Bringing Silo’s total raised to $272 million, the tranche is all the more impressive considering the cooling VC funding environment for supply chain startups. According to a report by Business Insider, funding for the sector reached only $3.3 billion in Q3 2022 — a 56% decrease year over year and down 37% compared to the second quarter. Funding continued to drop in Q1 2023, reflecting the broader slowdown in tech (and, to a lesser extent, the Silicon Valley Bank crisis).
Braun says that the new cash will be put toward product development and R&D, particularly in the areas of logistics and workflow automation.
“We believe these areas of focus are key to building an intelligent supply chain and a more efficient marketplace,” he said. “Silo plans to continue product development of its platform in an effort to bring its holistic solutions to more businesses within the perishable food space.”
Financing will remain a major focus for Silo too. To complement the company’s Instant Pay product, which lets customers make and receive payments while automating reconciliation back to their accounting systems, Silo’s launching Cash Advance, a loan program for food supply chain businesses. First Citizens Bank is partnering with Silo to provide $100 million in debt to fund Cash Advance.
“These financing programs are helping small- and medium-sized businesses within perishable supply chains scale their operations, find stability in a rapidly consolidating landscape and compete at a level that has historically been set aside for only the elite, larger businesses within the industry,” Braun said. “Leveraging a combination of data insights and access to additional working capital, through financing, gives companies the confidence to execute on market opportunities that give them a stronger seat at a rapidly consolidating table.”
San Francisco–based Silo currently has an 84-person team. Braun expects it’ll grow to around 100 by the end of the year.
Silo raises $32M to help food supply chain companies manage their finances by Kyle Wiggers originally published on TechCrunch