One of the biggest challenges enterprises face is processing all the data that they gather, and — by extension — deriving insights from that data. According to a 2018 Gartner report, 87% of organizations have low business intelligence and analytics maturity. The situation hasn’t changed much in recent years, even as companies invest greater amounts of capital in data initiatives. A 2021 Databricks and MIT survey found that only 13% of organizations are delivering on their data strategy.
Wojciech Danilo and Sylwia Brodacka are well-acquainted with the struggle. The cofounders of Enso, they’ve authored film visual effects tools that help to simulate particles — a data-intensive process.
“On the surface, it might seem that the data processing needs for most businesses — like the financial, manufacturing or oil and gas sectors — are completely different from the needs of the visual effect industry. The reality is quite the opposite,” Danilo told TechCrunch via email. “In the creation of visual effects for motion pictures, we can use the example of sand particle simulation. [P]hotorealistic sand simulation requires … a table containing particle data (such as their color, speed or size) and modifying the table data between animation frames by simulating physical rules such as a gravity or inter-particle collision rules and attraction forces … [T]tables can contain millions of records for each of the particles, which requires a highly efficient computational engine.”
Danilo and Brodacka had the idea of applying their visual effects tools, which were fundamentally data processing frameworks, to other domains including credit risk scoring modeling. This, in turn, led them to launch Enso, a data analysis and visualization startup that today came out of stealth with $16.5 million in funding from SignalFire, Khosla Ventures, Day One Ventures, Decacorn Capital, Y Combinator, Samsung Next, Harvard’s Endowment, West Coast Endeavors, Innovation Nest and others.
Danilo says that the capital is being put toward improving Enso’s platform with better documentation and onboarding, increasing the number of data processing modules on the said platform and releasing a software-as-a-service product called Enso Cloud, a fully managed offering, which is scheduled to launch in Q1 2023. “We conducted several successful pilots with banks and insurance companies,” Danilos said. “This … funding allows us to double down on bringing Enso Cloud to the market as early as next year.”
Processing data at scale
Danilo is a serial entrepreneur, having launched startups including visual effects tools creation platform Flowbox and simulator graphics firm Coddee. He worked with Brodacka at Flowbox, where Brodacka was responsible for designing and developing image processing libraries for processors and graphics cards.
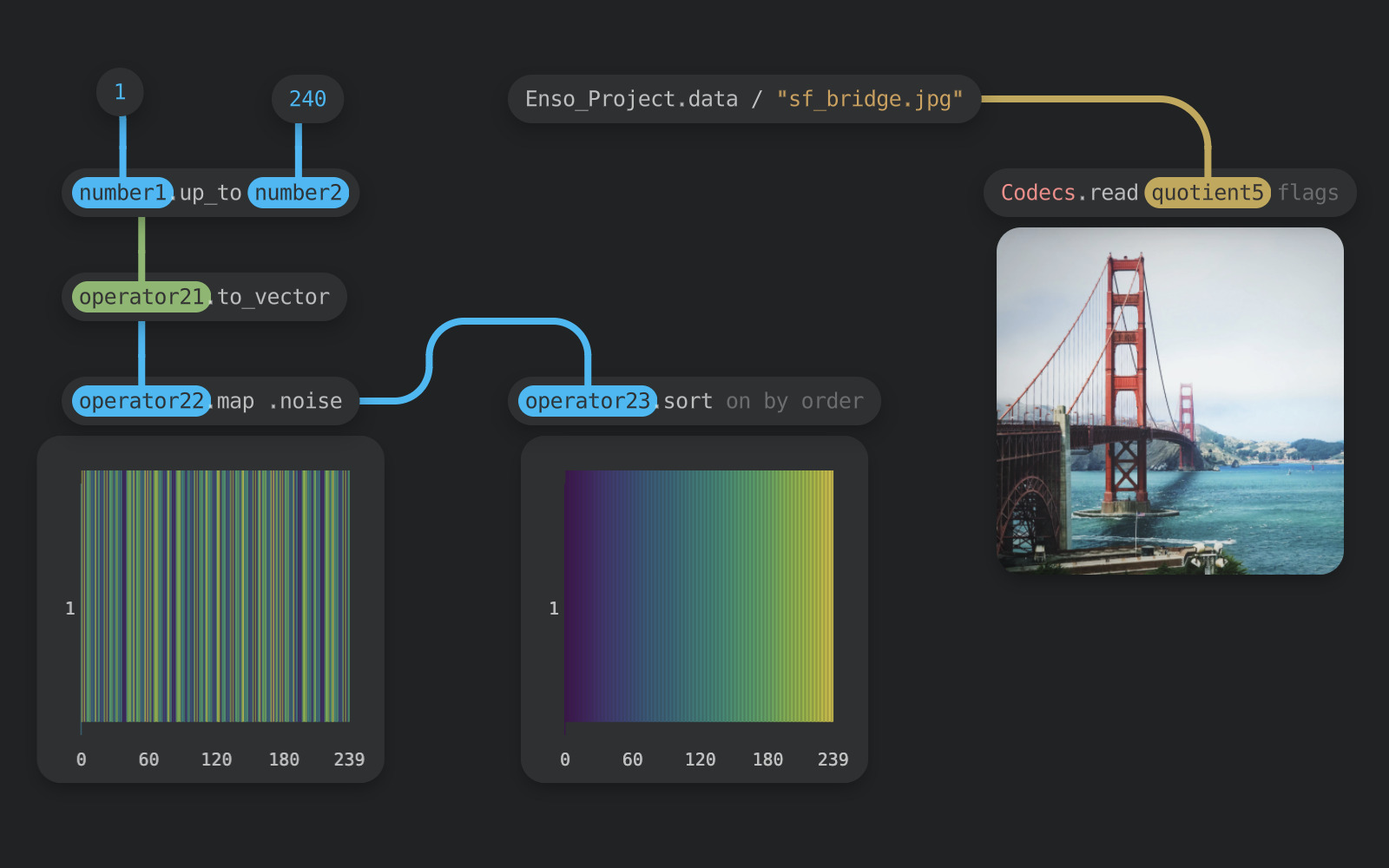
Enso’s platform enables data analytics.
Together, Danilo and Brodacka created Enso’s first product: the eponymous open source project Enso. A visual programming toolkit comprising components that process data and output results, Enso is designed to help build data workflows, dashboards and apps by analyzing historical and live data, suggesting possible next steps, displaying related examples and even controlling other applications.
While the concept might sound similar to existing visualization tools like Tableau Prep, Alteryx, Knime or Databricks, Danilo insists that Enso is different — and not simply a business intelligence “toy.”
“[I]n reality, Enso is revolutionizing much broader categories of data processing. Unlike other visual data processing software, [There’s more to it than a] nice interface with a hardcoded, limited and hardly-extensible set of components,” Danilo said. “Business users and data analysts are able to use Enso to perform self-service data analysis and process automation, while data scientists and developers can easily extend it to support more use cases highly tailored to their needs. A good example of such extensibility is our community — there are people who extended Enso with the possibility to analyze and process 3D models of buildings, sound and even internet of things device networks.”
Other standout features of Enso, according to Danilo, include its handling of data pipelines. Enso allows pipelines to be reviewed, versioned and deployed using a standard computer science toolset. Beyond this, Enso can help visualize errors when they occur and even prevent certain errors from happening, for example by preventing users from overriding values in a database.
One company that engaged Enso for a pilot project used the platform to discover duplicate transactions and provide automatic refunds to affected customers. This involved scraping data from multiple different sources, including government websites without APIs, and reconciling the data even in the absence of timestamps.
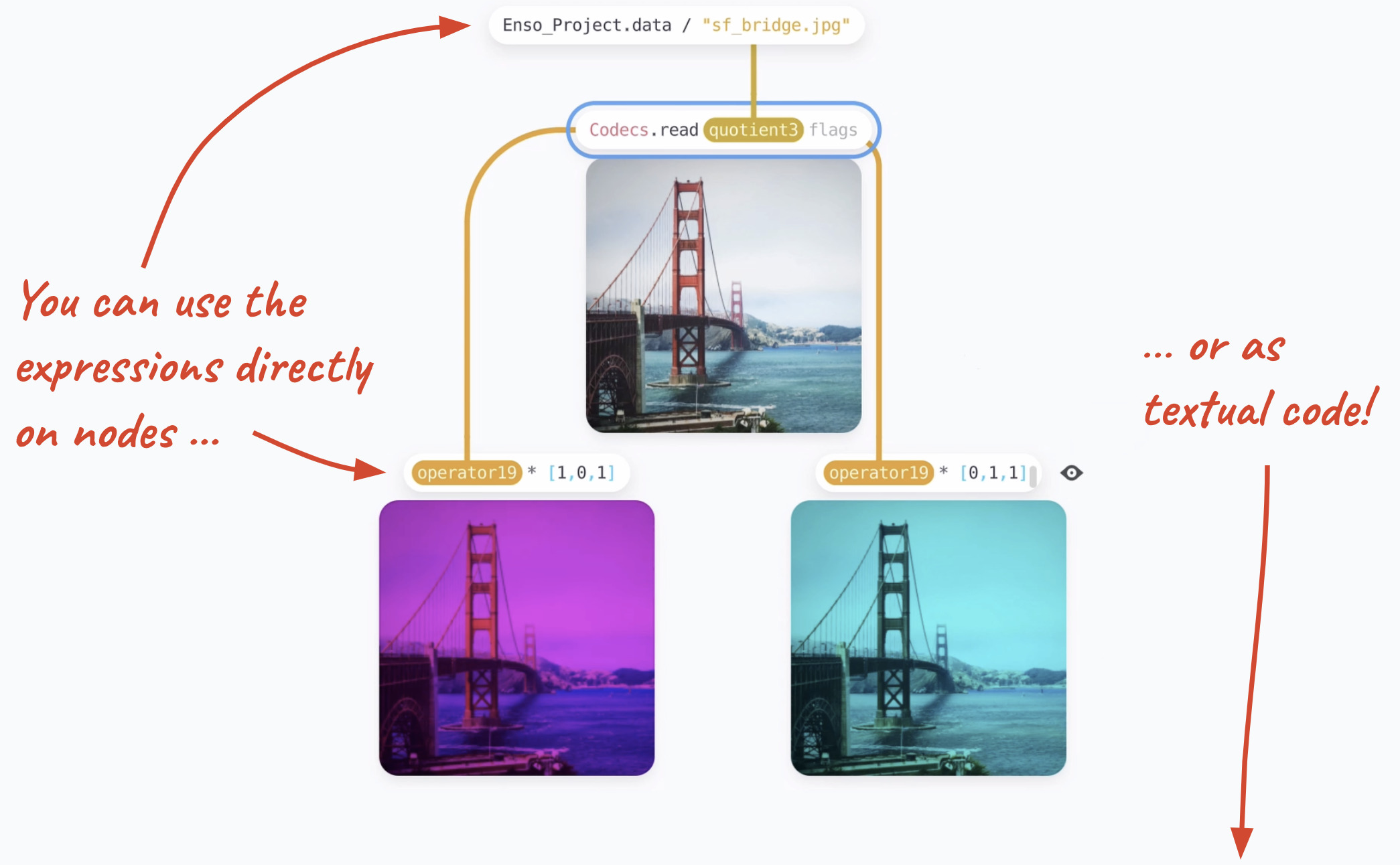
Image Credits: Enso
“Business users bring domain expertise to the table, but due to lack of technical skills, they need to constantly ask developers for help and, thus, are waiting for results even several days after every such request … We want Enso to become the standard data processing platform in the future,” Danilo said. “Currently, if you have a set of numbers and you want to crunch them, your default solution is a spreadsheet. However, if you want to process more advanced data, like logs, medical images, internet of things devices signals or your website traffic data, Excel is not enough. We want Enso to become the go-to solution.”
Building for the future
As data analysts and scientists become increasingly bogged down in repetitive work like updating spreadsheets every time a dataset changes, it’s Danilo’s hope that Enso ultimately reduces the barrier to more versatile forms of data processing. He has a business motivation, of course — Enso’s focus over the next year will be establishing a recurring revenue stream with Enso Cloud. But as someone who’s worked with large datasets and data pipelines for most of his career, he says he hopes to make the field less intimidating for the layperson.
“We believe that it is impossible to provide tools for this domain that do not base on a powerful and flexible engine. That is why Enso, in contrast to practically every other startup in this space, did not create just a nice interface with a hardcoded set of data-processing components,” Danilo said. “Instead, we started with building [a] data processing language and right now, we are focusing on building the user-friendly GUI layer on top of it.”
In total, San Francisco-based Enso, which has a 20-person workforce, has raised $17.5 million in capital. The company is actively hiring.