Casual mobile games have reached a fever pitch of interest with consumers, and so too with investors, who are rushing to back the biggest and most promising startups building these quick hits of engagement and diversion. In the latest development, a startup out of London called Tripledot — the company behind a popular Solitaire app, another game called Woodoku (‘wood blocks meet sudoku’), and more — is today announcing that it has raised $116 million. The funding puts the London-based startup’s valuation at $1.4 billion.
The round is being led by 20VC, the firm started by Harry Stebbings, who came into the world of investing initially via his popular 20 minute VC podcast, first teaming up to start VC Stride and eventually starting a fund named after his show (and raising some serious money to run it). Others in the round include Access Industries, Lightspeed Venture Partners and Eldridge, and the round follows a $78 million Series A in April 2021.
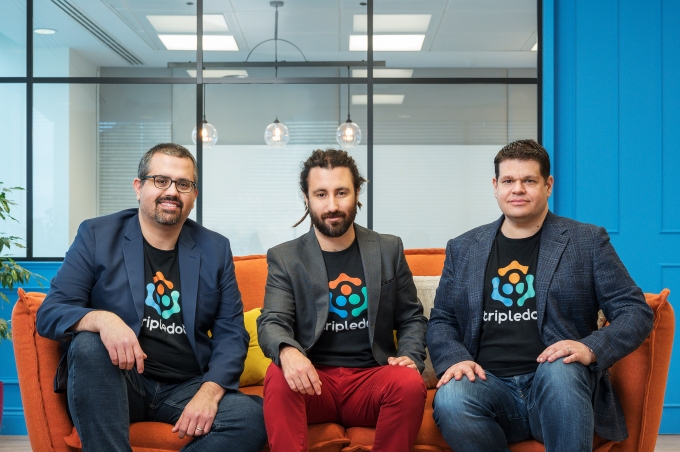
As with that Series A, this is a substantial raise for a Series B round, and Lior Shiff — the CEO who co-founded the company with Akin Babayigit (COO) and Eyal Chameides (CPO) — noted that it’s not to run the core business. Tripledot has been profitable since the end of its first year of operation (it was founded in 2017), now has close to 30 million monthly active users across its titles, and last year tripled revenues (without disclosing the actual figure).
“This fundraising is for M&A,” he told TechCrunch in an interview. Specifically, the plan is to acquire interesting startups working on creative ideas, to complement what Babayigit describes as a particularly strong set of skills that Tripledot has gained in developing engaging monetization mechanics and scaling games.

“We’ve gotten to the point of having a lot of technology and expertise that we can now leverage, so we want to buy studios, and use our platform to take those great games to reach a much larger audience,” Shiff added. “We are very good operators.” That’s not to say that Tripledot doesn’t have its own strong in-house game makers, he added, “but many of our peers excel in making great games but not how to reach large audiences, or to scale them into sustainable businesses. Now this capital gives us firepower.”
Dream Games, a big name among casual gaming startups at the moment (and as it happens one of Babayigit’s angel investments) likes to say that its ambition is to become the next Pixar. “Well, we’d like to be the next Activision Blizzard,” Shiff said.
Casual games and their ascendancy as a popular medium (and their success as startups) isn’t new news: Peak Games sold to Zynga for $1.8 billion in 2020, which you could say was one of high watermark events to put the business opportunity, and specific technical execution needed, for casual games on the map. Following that, Turkey’s Dream Games (founded by Peak alums) has been growing quickly and earlier this year raised $255 million to continue its run. Homa Games — which makes a platform for third parties to develop publish casual games (thus somewhat of a competitor to Tripledot) — raised $50 million this past October. And Spyke, another one from the Turkey Peak stable, raised big money in January based on the pedigree and track record of their founders, before even launching a single title.
All the same, the subject of just how popular a casual game can become, how they can loop in in audiences that you don’t traditionally think of a gaming demographics, and how sometimes creating something that is the exact opposite of a calculated business decision and finding massive success from that all came into sharp focus, and gave some pause for thought, earlier this year with the emergence of Wordle, a very simple word puzzle that went stratospherically viral in January.
Started as a puzzle written for his partner by developer Josh Wardle, Wordle only ever existed on Wardle’s website (no app), and never paid for or made any kind of marketing effort, and yet in its simplicity, scarcity (only one puzzle every 24 hours) and just the right amount of challenge/reward mechanics, it took off and found fans among grannies, school kids and everyone in between. (My friend’s elderly mother plays it on a computer and shares her results only through very blurry photos she takes of her monitor since she doesn’t use a smartphone.)
As Wardle told us in an interview in January, he had some inbound calls from investors, but really was more surprised than prepared to think of what to do next (save for making sure the game could manage the sudden onslaught of traffic it was sending to servers) since he didn’t want to turn it into a “business.”
In the end, he sold Wordle to the New York Times, which is now hosting it and will fold it into its own quiet word-puzzle-based casual gaming empire (which is fitting, as it served as some of the inspiration for building Wordle in the first place).
Shiff said Tripledot didn’t consider buying Wordle but its founders respected what it highlighted about the use cases and possibilities of casual games.
“It’s my mom, my aunt, who are playing these,” he said. “They would never say they’re gamers but will spend an hour on these. Maybe for a mental break, or while waiting for the dentist, historically they might have used puzzle books but now play on their phones.”
Babayigit noted that Tripledot doesn’t have any plans to develop web-only games, or to put out titles simply for building audience without specific business purpose — all potential “lessons” one might take from the likes of Wordle: which at the end of the day was perhaps partly attractive for being a kind of unicorn — not the $1 billion startup kind, but the kind that exist in a bubble free of the trappings of reality where games need to make money to continue to be viable. One lesson it did take is that there seem to be many more avenues left for development and variation in the longer run.
“I think casual games are still underserved,” said Babayigit. “The recent launches of Dream, Wordle and others have unleashed 2 billion gamers into the world, and we think that people are now looking for other types of experiences and games. Wordle actually proves that. So many more games can be built for those audiences, it’s still pretty crazy.”
And this is what the investors see, too.
“Tripledot’s growth rate and efficacy in building successful and highly retentive games is unmatched,” said Stebbings. “The leadership of Tripledot is singular; they have built an operation that has been scaling up rapidly while keeping its commitment to quality and a great company culture that knows how to attract and retain the best talents in gaming. We are looking forward to being part of the Tripledot journey.”