Blackshark.ai, the Austrian startup behind the digital globe you fly over in Microsoft’s Flight Simulator, has raised a $20M round A to develop and scale its replica-Earth tech. The potential applications for a planetary “digital twin” are many and various, and the company has a head start even on mapping giants like Google.
The world got a glimpse of a fully traversable and remarkably (if not 100%) accurate globe in Flight Simulator last year; we called a “technical marvel” and later went into detail about how it was created, and by whom.
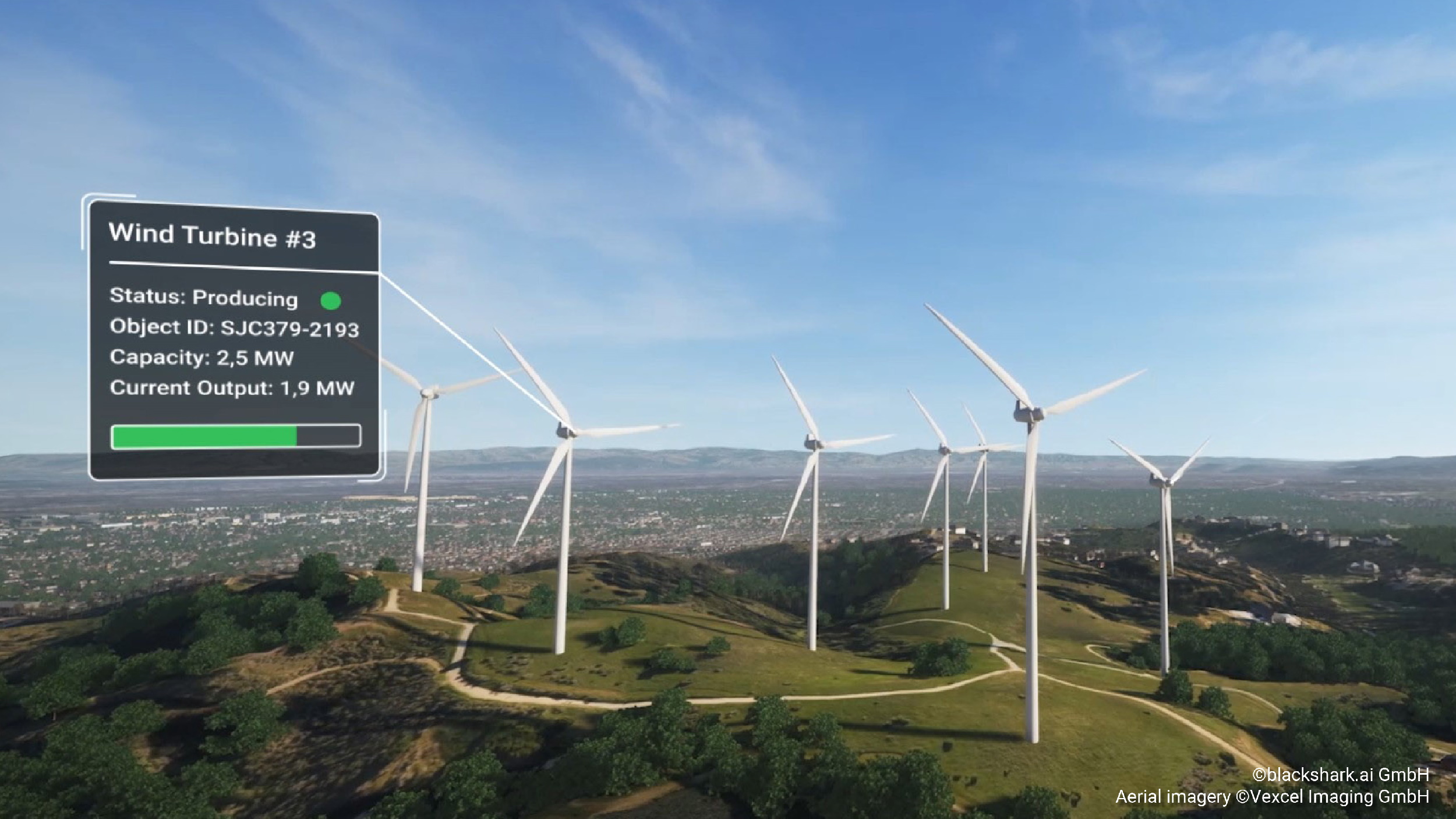
Blackshark.ai was spun out of gaming studio Bongfish with the intention, founder and CEO Michael Putz told me, of taking their world building technology beyond game environments. The basis of their technique is turning widely available 2D imagery into accurate 3D representations with machine learning, a bit of smart guesswork, and a lot of computing power.
The details are here, but essentially the blackshark.ai system has a canny understanding of what different buildings look like from above, even in sub-optimal lighting and incomplete imagery. The machine learning system they’ve built can extrapolate from imperfect outlines by considering the neighborhood (residential vs commercial), roof type (slanted vs flat), and other factors like the presence of air conditioning units and so on. Using all this it creates a plausible 3D reconstruction of the building.
The hard part, of course, isn’t how to do that once but how to do it a billion times on a regular basis, in order to create an up-to-date 3D representation of every building on the planet. As Putz explained: “Even if you could afford to buy all the computing power for this, building the backend to serve it is hard! This was a real world issue we had to deal with.”
Their solution, as is often necessary for AI-powered services, was to optimize. Putz said that the process of calculating the 3D model for every building on the planet originally took about a month of computation, but now can be done in about 3 days, an acceleration of about 300x.
Having this ability to update regularly based on new imagery from satellites is crucial to their business proposition, Putz explained. A lot of 3D map data, like what you see in Google and Apple’s maps, is based on photogrammetry, aerial photography combining multiple aerial images and comparing parallax data (like our eyes do) to determine size and depth. This produces great data… for when the photo is taken.
If you want your 3D map to represent what a block in Chicago looked like last week, not two years ago, and you want to provide that level of recency to as much of the globe as possible, the only option these days is satellite imagery. But that also necessitates the aforementioned 2D-to-3D method.
Putz noted that although the blackshark.ai 3D map and those from Google and Apple have superficial similarities, they’re not really competitors. All provide a realistic “canvas,” but they differ greatly in intention.
“Google Maps is the canvas for local businesses,” he said, and what’s important to both the company and its users is locations, reviews, directions, things like that. “For us, say for flooding, a climate change use case, we provide the 3D data for say, Seattle, and others who specialize in water physics and fluid simulation can use the real world as a canvas to draw on. Our goal is to become a searchable surface of the planet.”
What’s the total flat rooftop area available in this neighborhood of San Diego? What regional airports have an open 4,000-square-meter space? How do wildfire risk areas overlap with updated wind models? It’s not hard to come up with ways this could be helpful.
“This is one of those ideas where the more you think about it, the more use cases come up,” Putz said. “There’s obviously government applications, disaster relief , smart cities, autonomous industries — driving and flying. All these industries need synthetic environments. This wasn’t just like, ‘hey we want to do this,’ it was needed. And this 2D-3D thing is the only way to solve this massive problem.”
The $20M round was led by M12 (Microsoft’s venture fund) and Point72 Ventures. Putz was excited to have a few familiar faces advising board: Google Earth co-founder Brian McClendon, former CEO of Airbus Dirk Hoke, and Qasar Younis, former Y Combinator COO and now CEO of Applied Intuition. (These folks are advising, not joining the board, as this paragraph mistakenly had earlier.)
Scaling is more a matter of going to market rather than building out the product; while of course more engineers and researchers will be hired, the company needs to go from “clever startup” to “global provider of 3D synthetic Earths” in a hurry or it may find some other clever startup eating its lunch. So a sales and support team will be built out, along with “the remaining pieces of a hyperscaling company,” Putz said.
Beyond the more obvious use cases he listed, there’s a possibility of — you knew it was coming — metaverse applications. In this case however it’s less hot air and more the idea that if any interesting AR/VR/etc applications, from games to travel guides, wanted to base their virtual experience in a recently rendered version of Earth, they can. Not only that, but worlds beyond our own can be generated by the same method, so if you wanted to scramble the layout of the planet and make a new one (and who could blame you?) you could do so by the end of the week. Doesn’t that sound nice?
Once the new funding gets put to use, expect to see “powered by Blackshark.ai” or the like on a new generation of ever more detailed simulations of the complex markets and processes taking place on the surface of our planet.